Advertisement
Journals
Science
- Volume 377
- Issue 6609
- 26 Aug 2022


COVER This image inspired by Bronze Age art depicts people of diverse cultures spreading their genes between West Asia and Southeast Europe. From left to right: Mycenaean, Minoan, Hittite, Armenian, and Urartian. A total of 1317 ancient genomes spanning 10,000 years were analyzed to reveal the manifold connections between these regions that are invisible in modern DNA. See pages 908, 922, 939, 940 and 982.
Credit: Oliver Uberti Creative
Science Advances
- Volume 8
- Issue 34
- 26 Aug 2022


ONLINE COVER Closeup of FIND-IT barley. Global demand for food is driving improved agricultural productivity. Knudsen et al. demonstrate FIND-IT, an approach to rapidly develop resilient crop plants and improve microbial production systems. The method allows for selection and incorporation of domestication traits into the approximately 7000 undomesticated or semidomesticated crop plants that have superior drought tolerance, water tolerance, disease resistance and mineral use efficiency. Using cereal crop barley, the researchers show that FIND-IT can potentially serve as tool to help meet future food demands.
Credit: Chistoph Dockter, Calsberg Research LaboratoryScience Immunology
- Volume 7
- Issue 74
- Aug 2022
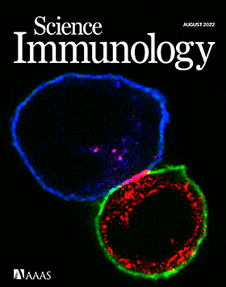
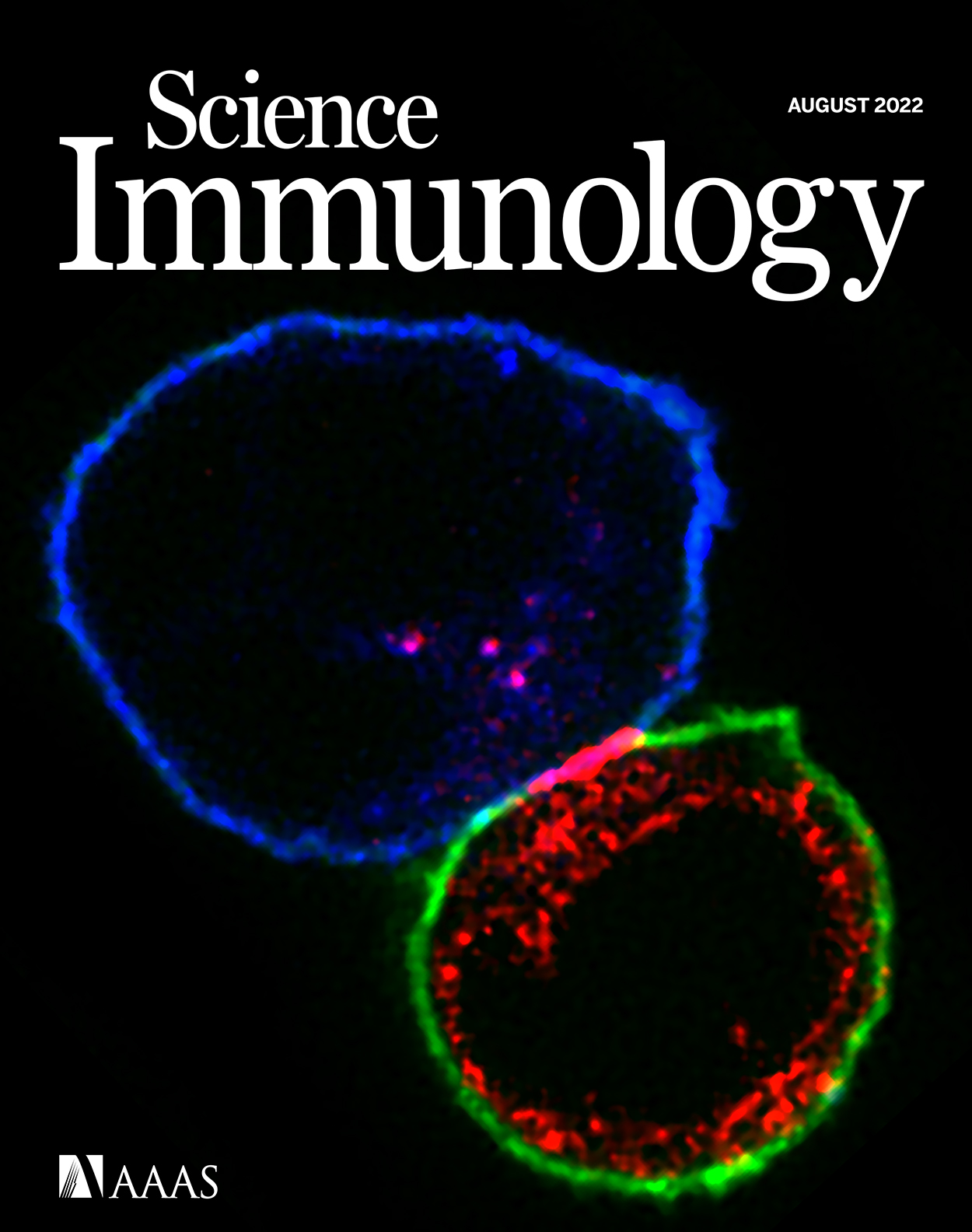
ONLINE COVER Exclusion of CD45 from a CAR-T Synapse. This month’s cover features a confocal microscopy image in which a human T cell expressing a CD19-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), stained in red, has formed an immunological synapse with a human Raji B cell lymphoma cell (blue). CD45 (green), a bulky tyrosine phosphatase enzyme that can inhibit CAR-T activation, is effectively excluded from the central portion of this synapse. Xiao et al. developed a size-exclusion model to explain how the relative sizes of the CAR construct and the CD45 isoform on a CAR-T cell and the target antigen on a tumor cell calibrate CD45’s dampening of antigen-triggered CAR-T activation at the synapse.
Credit: Xiaolei Su/Yale UniversityScience Robotics
- Volume 7
- Issue 69
- Aug 2022
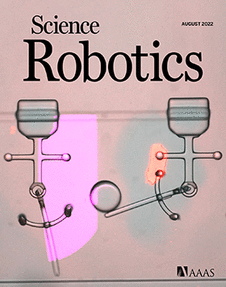
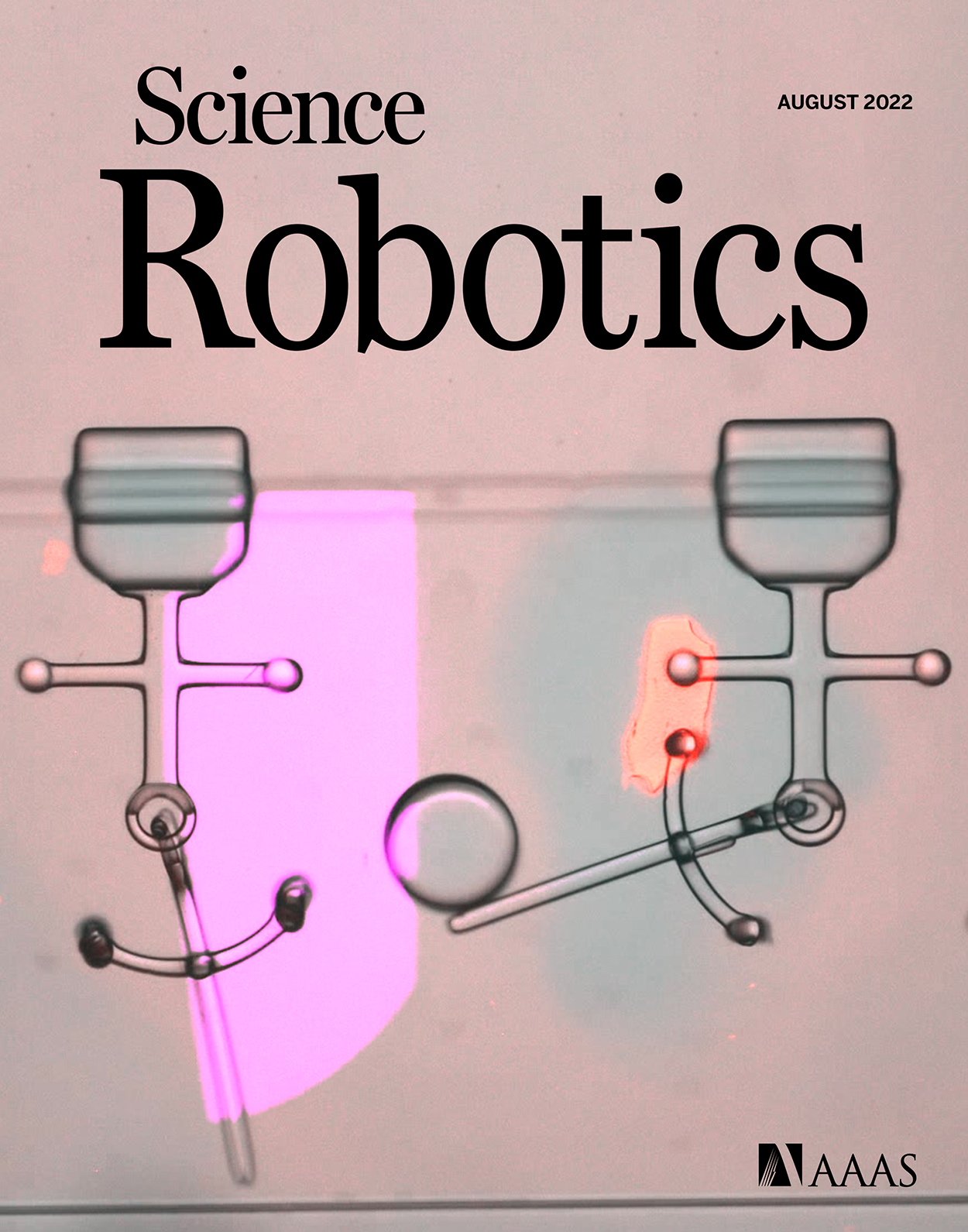
ONLINE COVER Flexing Biomolecular Muscle. Actuation of soft microrobots can be achieved through the application of miniature motors, such as artificial muscles. However, the integration of such actuators within soft microrobots requires assembly processes that are often slow and require multiple steps. Wang et al. have developed a rapid and cost-effective in situ fabrication process that integrates artificial muscles composed of molecular motors in a variety of microrobots. This month’s cover shows a microrobot manipulating a ball; its arms are sequentially controlled by light-responsive artificial muscles.
Credit: Wang et al./Osaka UniversityScience Signaling
- Volume 15
- Issue 748
- 23 Aug 2022
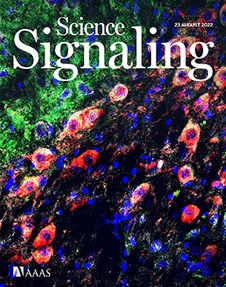
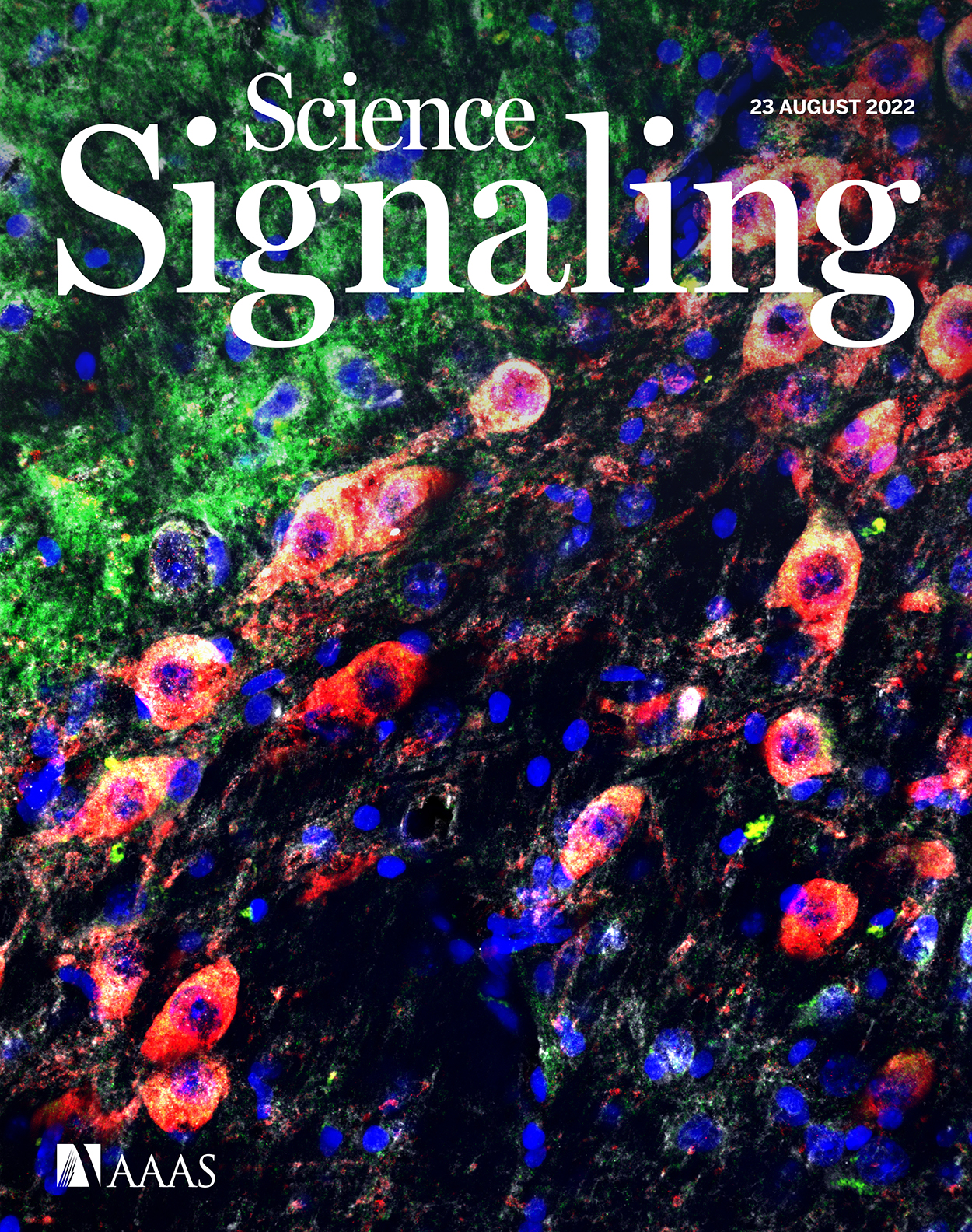
ONLINE COVER This week, Zhang et al. report a regulatory loop between the intracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein and the kinase LRRK2. The loop promoted neuronal loss and other disease markers in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease that were reduced with the APP-processing inhibitor itanapraced. The image shows staining for markers of autophagy (green) and dopaminergic neurons (red) in brain tissue from LRRK2-mutant mice.
Credit: Zhang et al./Science SignalingScience Translational Medicine
- Volume 14
- Issue 659
- 24 Aug 2022
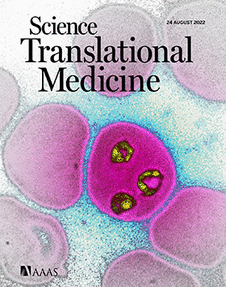
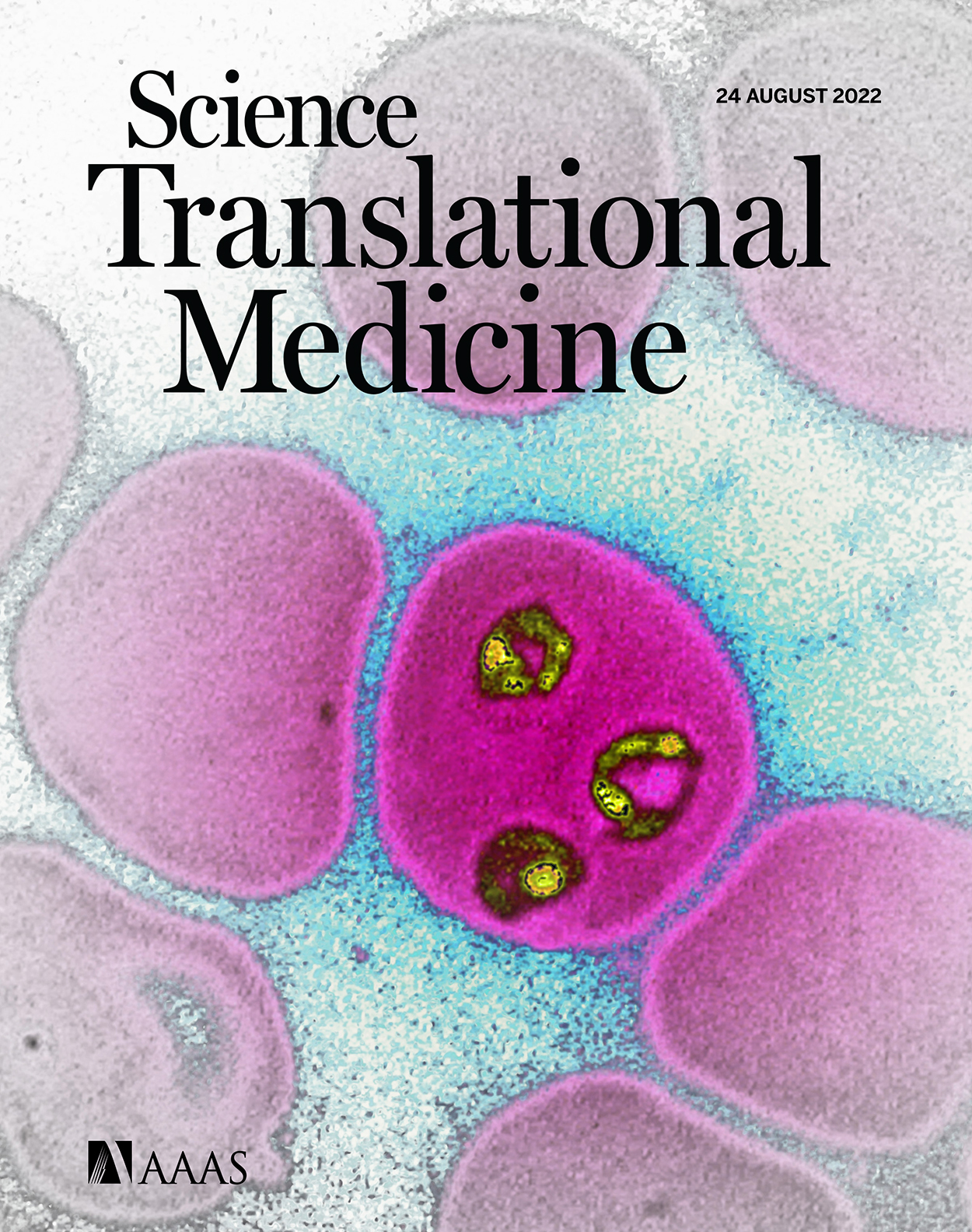
ONLINE COVER Genetically Attenuated Parasites. The cover image shows a color-enhanced light micrograph of ring-stage Plasmodium falciparum (yellow), one of the species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans, inside of a human erythrocyte. A safe and effective malaria vaccine is essential to curb the morbidity and mortality caused by P. falciparum infection. Murphy et al. evaluated the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of a genetically attenuated P. falciparum with deletions of the P52, P36, and SAP1 genes (PfGAP3KO). Malaria-naïve volunteers were vaccinated with PfGAP3KO sporozoites via mosquito bite delivery. The authors found that PfGAP3KO vaccination provided protection against controlled human malaria infection, supporting further clinical evaluation of this vaccine candidate.
Credit: James Cavallini/Science SourceScience Partner Journals
The Open Access journal Research, published in association with CAST, publishes innovative, wide-ranging research in life sciences, physical sciences, engineering and applied science.
The Open Access journal Plant Phenomics, published in association with NAU, publishes novel research that advances plant phenotyping and connects phenomics with other research domains.
The Open Access journal BMEF, published in association with SIBET-CAS, is a platform for the multidisciplinary community of biomedical engineering, publishing wide-ranging research in the field.
The Open Access journal BioDesign Research, published in association with NAU, publishes novel research in the interdisciplinary field of biosystems design.
The Open Access journal Advanced Devices & Instrumentation, published in association with BIACD, is a forum to promote breakthroughs and application advances at all levels of electronics and photonics.
The Open Access journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, published in association with BIT, promotes the knowledge interchange and hybrid system codesign between living beings and robotic systems.
The Open Access journal Energy Material Advances, published in association with BIT, is an interdisciplinary platform for research in multiple fields from cutting-edge material to energy science.
The Open Access journal Space: Science & Technology, published in association with BIT, promotes the exploration and research of interdisciplinary sciences in the space field.
The Journal of Remote Sensing, an Open Access journal published in association with AIR-CAS, promotes the theory, science, and technology of remote sensing, as well as interdisciplinary research within earth and information science.
The Open Access journal Health Data Science, published in association with PKU, aims to advance the horizon of health data science through transdisciplinary learning, communication, and collaboration with health practitioners and policymakers.
The Open Access journal Ultrafast Science, published in association with XIOPM, publishes cutting-edge and emerging topics in ultrafast science with broad interest from scientific communities.
The Open Access journal Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (OLAR), published in association with SML-ZHUHAI, publishes technologically innovative research in marine, terrestrial, and atmospheric studies and the interactions among them.
The Open Access journal Intelligent Computing, published in affiliation with Zhejiang Lab, publishes the latest research outcomes and technological breakthroughs in intelligent computing.
