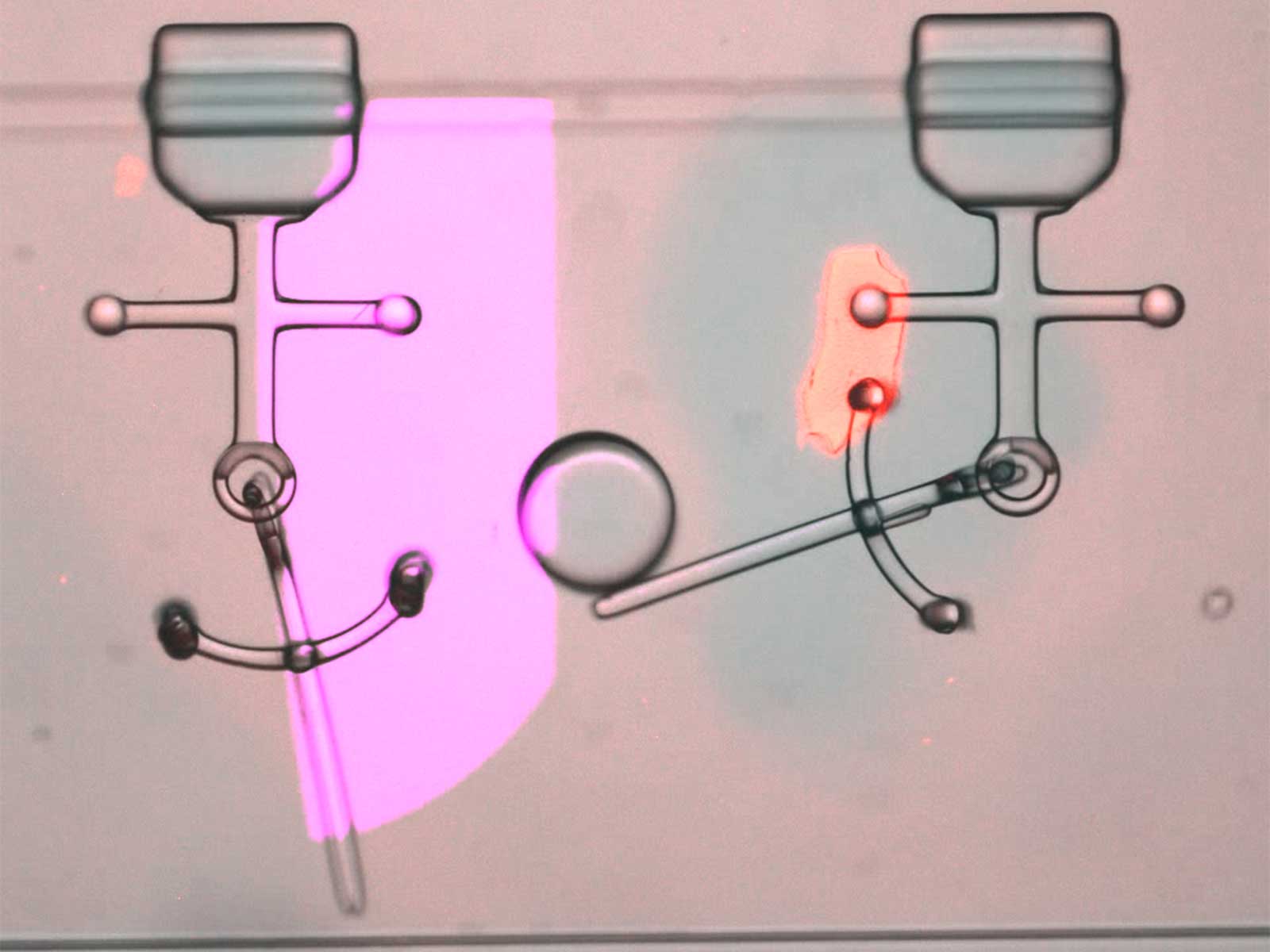
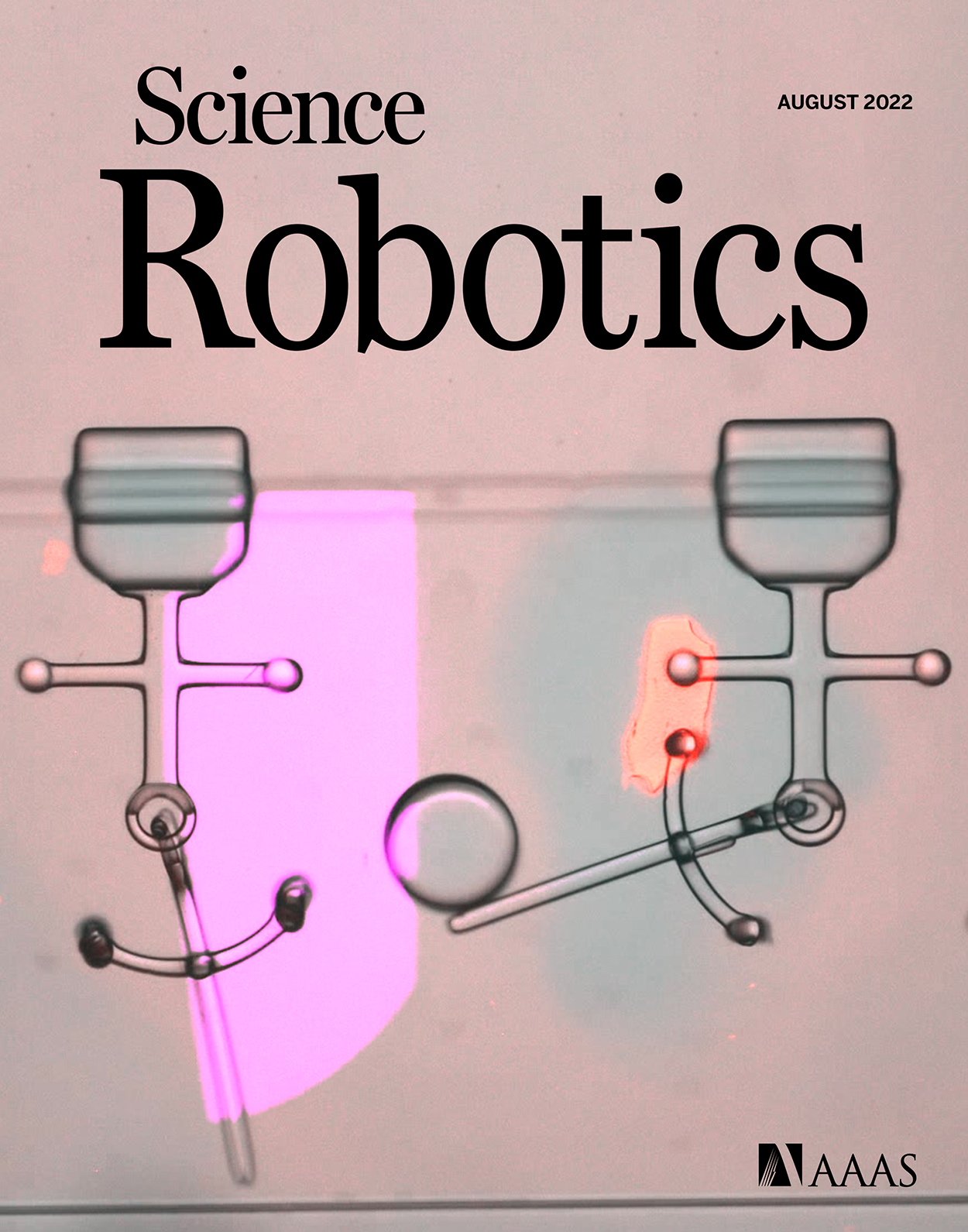
ONLINE COVER Flexing Biomolecular Muscle. Actuation of soft microrobots can be achieved through the application of miniature motors, such as artificial muscles. However, the integration of such actuators within soft microrobots requires assembly processes that are often slow and require multiple steps. Wang et al. have developed a rapid and cost-effective in situ fabrication process that integrates artificial muscles composed of molecular motors in a variety of microrobots. This month’s cover shows a microrobot manipulating a ball; its arms are sequentially controlled by light-responsive artificial muscles.
Credit: Wang et al./Osaka UniversityScience Robotics
- Volume 7|
- Issue 69|
- Aug 2022
ONLINE COVER Flexing Biomolecular Muscle. Actuation of soft microrobots can be achieved through the application of miniature motors, such as artificial muscles. However, the integration of such actuators within soft microrobots requires assembly processes that are often slow and require multiple steps. Wang et al. have developed a rapid and cost-effective in situ fabrication process that integrates artificial muscles composed of molecular motors in a variety of microrobots. This month’s cover shows a microrobot manipulating a ball; its arms are sequentially controlled by light-responsive artificial muscles.
Credit: Wang et al./Osaka University